Network Infrastructure

Network infrastructure is the foundation of any IT ecosystem, enabling communication, data exchange, and resource sharing across devices and systems. With the rapid expansion of digital transformation, robust and scalable network infrastructure has become essential for businesses, governments, and individuals. This article explores the components, design principles, and importance of network infrastructure in today’s interconnected world.
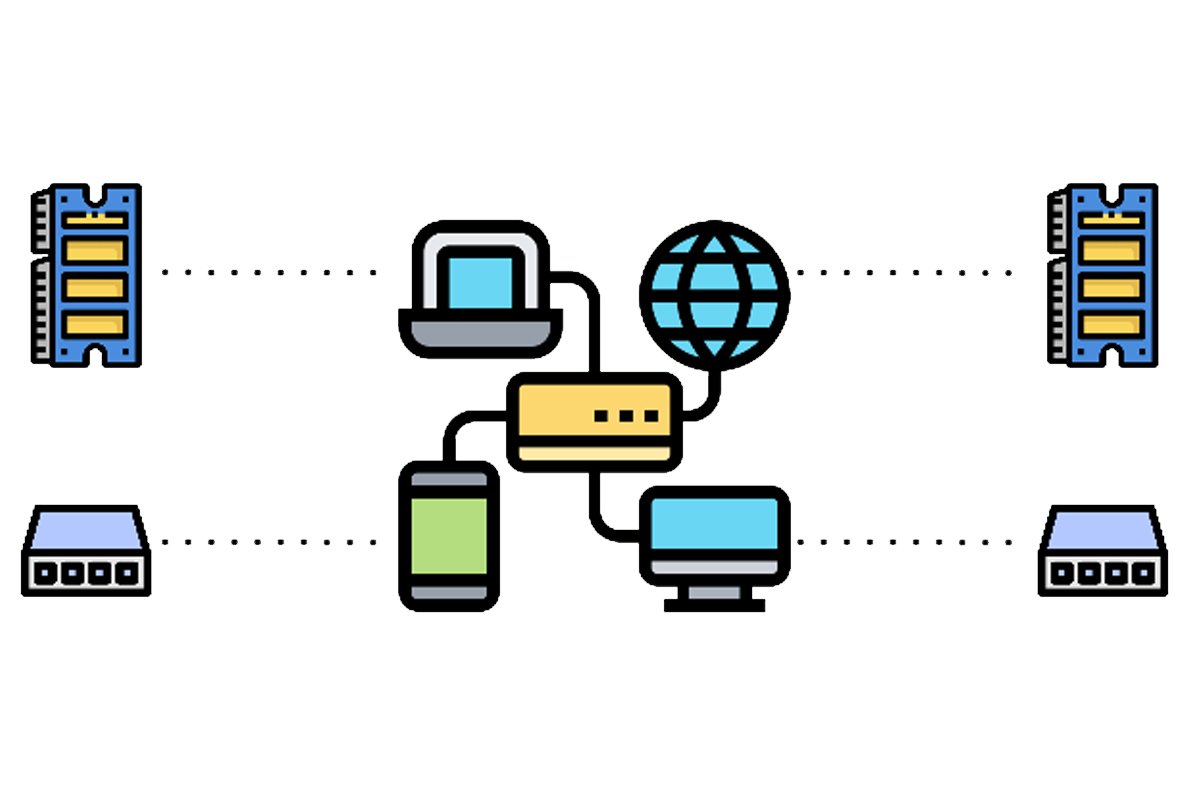
What Is Network Infrastructure?
Network infrastructure refers to the hardware, software, and protocols that enable devices to connect, communicate, and share resources. It includes physical components like routers, switches, and cables, as well as virtual technologies like cloud-based networks and software-defined networking (SDN).
Key Components of Network Infrastructure
A complete network infrastructure is built using various components, each serving a specific purpose:
Hardware
- Routers: Direct data packets between networks, connecting devices to the internet or other networks.
- Switches: Enable communication within a local network by connecting multiple devices.
- Access Points: Extend wireless connectivity to devices within a specific area.
- Cabling: Ethernet cables, fiber optics, and coaxial cables facilitate physical connections.
- Servers: Host applications, manage data, and provide centralized control.
Software
Network Operating Systems: Manage hardware components and network operations.
- Network Management Tools: Monitor performance, troubleshoot issues, and optimize resources.
- Virtual Network Functions (VNFs): Replace physical hardware with virtualized network services for flexibility and scalability.
Connectivity
- Protocols: Rules like TCP/IP, DNS, and HTTP govern how data is transmitted and received.
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs): Provide access to external networks, including the internet.
Types of Network Infrastructure
Local Area Network (LAN)
LANs connect devices within a confined area, such as an office or home. They are typically faster and more secure than broader networks.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
WANs span large geographic areas, connecting multiple LANs. The internet is the largest example of a WAN.
Wireless Networks
Wireless technologies like Wi-Fi and 5G provide mobility and flexibility without the need for physical cables.
Cloud Networks
Cloud-based network infrastructure allows businesses to deploy and manage resources over the internet, reducing hardware dependency.
Designing an Effective Network Infrastructure
Scalability
A network should be designed to accommodate growth in users, devices, and data traffic without significant overhauls.
Redundancy and Resilience
Implement redundant systems to ensure uptime in case of hardware failures or outages.
Security
Protect the network with firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Performance Optimization
Prioritize speed and reliability by using quality hardware, optimizing configurations, and managing bandwidth.
The Role of Emerging Technologies
Modern network infrastructure is evolving rapidly with the adoption of new technologies:
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): Enables centralized management and dynamic network configuration.
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): Reduces reliance on hardware by virtualizing network functions.
- Edge Computing: Processes data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance.
- 5G Technology: Delivers faster speeds and lower latency, revolutionizing wireless connectivity.

Challenges in Network Infrastructure
Despite its importance, network infrastructure comes with challenges:
- Cybersecurity Threats: Constantly evolving threats require proactive security measures.
- Cost Management: Maintaining and upgrading infrastructure can be expensive.
- Complexity: Managing a growing network with diverse technologies demands skilled personnel and advanced tools.
Future Trends in Network Infrastructure
The future of network infrastructure is being shaped by:
- AI and Automation: Tools that predict issues, optimize performance, and enhance security.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Increasing demand for infrastructure that supports billions of connected devices.
- Sustainability: Energy-efficient technologies and renewable power sources to reduce environmental impact.
Network infrastructure is the backbone of modern digital connectivity, empowering organizations to operate efficiently and innovate continuously. By leveraging advanced technologies, addressing challenges, and adopting scalable designs, businesses can build resilient networks that meet current demands and prepare for future growth.
Routing, Switching & Wireless Solution Vendors
UTP & Fiber Infrastructure Solution Vendors
Ready to elevate your business?
Get in touch with Intech for innovative IT solutions and expert consulting tailored to your success!”
contact us today and transform your business with Intech’s expert IT solutions!















